- Delhi
- Last Update 02:28: am

Understanding Business Analytics: Definition, Types, Salary and Examples
What is Business Analytics?
The process of obtaining, evaluating, interpreting, and visualizing data in order to produce insightful knowledge that supports well-informed decision-making inside a company is known as business analytics. To find patterns, trends, and correlations in data sets, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and machine learning approaches are used. Businesses can enhance overall business outcomes, find opportunities, improve performance, optimize processes, and reduce risks by utilizing business analytics. In order to deliver actionable insight for strategic planning, resource allocation, and gaining a competitive advantage in the marketplace, this discipline integrates data from multiple sources.
Components of Business Analytics
Business Analytics comprises several key components:
Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various sources including internal databases, external datasets, and online platforms.
Data Cleaning and Preparation: Refining raw data to ensure accuracy and consistency, often involving removing duplicates, handling missing values, and standardizing formats.
Data Analysis: Utilizing statistical techniques, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools to uncover insights and patterns within the data.
Predictive Modeling: Developing models to forecast future trends, behaviors, and outcomes based on historical data.
Data Interpretation and Reporting: Communicating findings and actionable insights to stakeholders through reports, dashboards, and presentations.
Types of Business Analytics
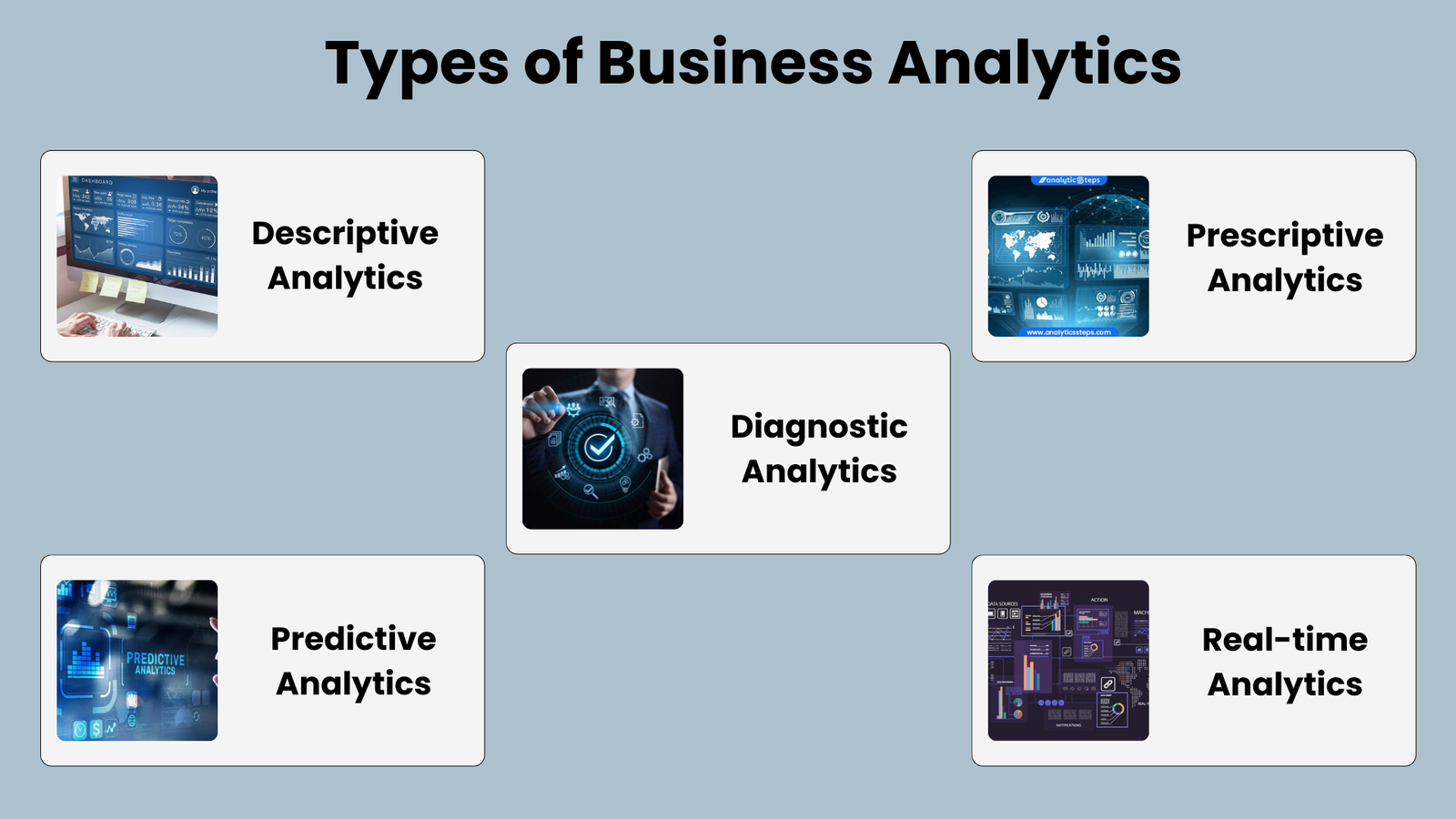
Business analytics can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving specific purposes within an organization. Here are some common types of business analytics:
Descriptive Analytics:
Descriptive analytics involves the examination of historical data to understand what has happened in the past. It focuses on summarizing data to gain insights into patterns, trends, and relationships. Techniques such as data aggregation, data mining, and visualization are often used in descriptive analytics.
Diagnostic Analytics:
The goal of diagnostic analytics is to determine the causes of specific occurrences. It involves deeper analysis of data to uncover the root causes of problems or successes. By analyzing historical data and relationships, diagnostic analytics helps businesses understand why certain outcomes occurred.
Predictive Analytics:
To predict future outcomes, predictive analytics makes use of statistical algorithms and historical data. It involves the use of techniques such as regression analysis, machine learning, and forecasting to make predictions based on patterns identified in past data. Predictive analytics helps businesses anticipate future trends and make informed decisions.
Prescriptive Analytics:
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond predicting future outcomes by suggesting possible actions to optimize results. It leverages advanced analytics techniques and optimization algorithms to recommend the best course of action based on predicted outcomes. Prescriptive analytics offers useful insights that assist firms in making data-driven decisions.
Real-time Analytics:
Real-time analytics involves the analysis of data as it is generated to provide immediate insights and support decision-making in real time. It often involves the use of technologies such as stream processing and in-memory analytics to analyze data as it flows into the system. Real-time analytics is particularly useful in industries such as finance, telecommunications, and online retail where timely decision-making is critical.
Business Analytics Process
Business analytics is a systematic process used by organizations to analyze data and derive actionable insights to make informed decisions and improve business performance. Usually, the procedure entails the following crucial steps:
Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the business problem or opportunity that needs to be addressed through analytics. This step involves understanding the organization's goals and identifying specific questions that need to be answered.
Data Collection: Gather relevant data from various sources, which may include internal databases, third-party data providers, surveys, social media, and other sources. At this point, ensuring the integrity and quality of the data is essential.
Data Preparation: Cleanse, transform, and pre-process the data to make it suitable for analysis. This may involve handling missing values, removing outliers, standardizing formats, and integrating data from different sources.
Data Exploration: Investigate the information to learn more about its features, connections, and trends. This can involve descriptive statistics, data visualization techniques, and exploratory data analysis (EDA) to identify trends, correlations, and outliers.
Data Modeling: Develop analytical models or algorithms to extract insights from the data. This may include statistical models, machine learning algorithms, predictive models, optimization techniques, and other analytical approaches.
Model Evaluation: Assess the performance of the analytical models using appropriate metrics and validation techniques. This step helps ensure that the models are accurate, reliable, and robust enough to make informed decisions.
Insights Generation: Interpret the results of the analysis to generate actionable insights that address the business objectives. This may involve summarizing findings, identifying key drivers, and highlighting recommendations for decision-makers.
Decision Making: Use the insights generated from the analysis to support strategic, tactical, and operational decision-making processes within the organization. This could involve implementing changes, optimizing processes, or launching new initiatives based on the findings.
Monitoring and Iteration: Continuously monitor the impact of decisions and interventions on business outcomes. Iterate the analytics process by incorporating feedback, refining models, and adapting strategies to changing business conditions.
Communication and Visualization: Communicate the results and insights derived from the analytics process effectively to stakeholders using clear and concise language, data visualization techniques, and storytelling methods. This helps ensure that insights are understood and acted upon across the organization.
Business Analytics Salary

The average salary for a Business Analyst in India ranges from Rs 400,000 to Rs 1,500,000 per annum, with an average of Rs 700,000 per annum. As you might expect, experience plays a big role in how much a Business Analyst makes. Business analysts with five to ten years of experience can earn up to Rs 900,000 annually, while entry-level analysts can expect to make between Rs 350,000 and Rs 500,000. Analysts with over 10 years of experience can command salaries exceeding Rs 1,500,000.
Location also plays a role in Business Analyst salaries. Big cities like Delhi tend to offer higher salaries than smaller towns.
Business Analytics Examples
- Working with data to determine the ideal pricing point for a product that a company is going to launch would be a basic example of business analytics. Many elements would need to be taken into account throughout this research project before a solution could be found.
- Using business analytics approaches to determine which consumers are most likely to cancel their subscriptions and in what quantity would be another example.
- Working with the data that is already accessible to determine how and why regular customers' tastes and preferences vary is one of the most well-liked applications of business analytics.
Conclusion
Business analytics stands as a pivotal discipline in modern organizations, facilitating informed decision-making through the meticulous extraction, analysis, and interpretation of data. By integrating various analytical techniques, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, businesses can glean invaluable insights to enhance performance, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities. Moreover, the structured business analytics process, from defining objectives to the communication of findings, ensures a systematic approach to deriving actionable insights. With the increasing demand for skilled professionals in this field, business analytics continues to play a vital role in shaping strategic initiatives and driving sustainable growth across industries.









